Not everyone enjoys music or silence like you might.
For most people, every day sounds like chewing, breathing, or music are just background noises. But for some, these sounds can trigger intense fear, anxiety, and even panic attacks.
These lesser-known audio phobias can greatly impact a person’s quality of life, making them avoid daily situations and experiences. While the exact causes are not always clear, these often stem from traumatic experiences, genetic factors, or environmental changes.
From the fear of loud noises to the dread of silence, here are the seven strange audio-related phobias you’ve probably never heard of.
1. Phonophobia: The Terror in the Decibels

Phonophobia, also called ligyrophobia and acousticophobia, is an unreasonable fear of loud noises, causing panic attacks and anxiety.
People with phonophobia may find normal sounds like car horns, door slamming, or even fireworks too much to handle.
This phobia is not caused by hearing loss or any type of hearing problem. Instead, it is a mental health condition that can start at any age. Genetic factors and bad experiences can play a role in how it develops.
Treatment options for phonophobia include exposure and response therapy. This slowly exposes the person to the feared sounds in a controlled setting so they can learn to manage their worry and stop avoiding everyday sounds.
2. Melophobia: The Horrors of Music

For most people, music brings joy and comfort. But those with melophobia feel the opposite.
Melophobia comes from the Greek words “melos” (music) and “phobos” (fear). It is a strong fear or dislike of music that can range from mild to severe.
This can make everyday life hard because music is common in many social settings, from restaurants to shopping malls. This can lead to social isolation and even physical health problems.
While treatment options are available, the widespread presence of music makes it a difficult phobia to overcome.
3. Misophonia: The Sounds That Drive You Crazy

Misophonia is a disorder where certain repetitive sounds, often related to eating, breathing, or chewing, cause intense emotional reactions like anger or the need to escape.
These reactions can be so severe that they make it hard for a person to function in social situations.
Researchers think that those with misophonia may already have issues with how their brains filter sounds. They have found that the anterior insular cortex (AIC) is a key brain region involved in misophonia. It shows increased activity in response to trigger sounds.
Whole-brain MRI scans have also shown that people with misophonia have higher amounts of myelination. Myelin is a fatty substance that wraps around nerve cells in the brain. However, it is not yet known if this extra myelin is a cause or an effect of the disorder.
4. Sedatephobia: The Dread of Silence

Sedatephobia, coming from the Greek roots “sedate” (quiet, asleep, or dead) and “phobos” (fear), is the intense fear of silence.
Bad experiences associated with a lack of noise can contribute to the development of sedatephobia. An example of this is being locked in a quiet room as punishment during childhood.
But, researchers have said that the growing dependence on constant noise in the modern world may also play a role. The contrast between constant stimulation and sudden silence can be unsettling for some people.
“In the 21st century, we are bombarded by noise all the time. Everywhere we go, there is music, computers, mobile phones, ring tones, buzzers, conversation, people, and television screens.” says Dominic Knight, a Clinical Hypnotherapist.
“This technological revolution has had the side-effect of creating a group of people who find silence unsettling and uncomfortable. These patients report an unhealthy need for constant noise and interaction with others. This can cause serious problems in their lives.”
5. Earachnophobia: The Stuff of Nightmares
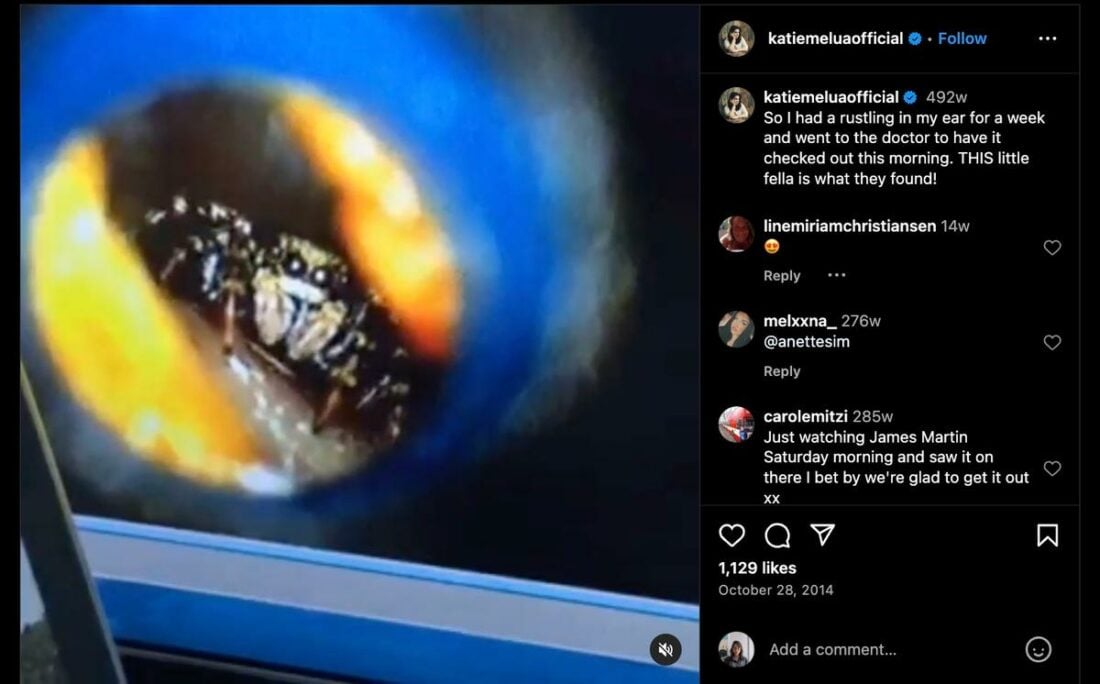
Earachnophobia is the fear of spiders or other insects crawling into one’s ear.
It gained attention after singer Katie Melua discovered a spider had been living in her ear for a week. While the chances of this happening are slim, just the thought can cause intense worry for those with this phobia. That’s why this can also be triggered when wearing in-ear monitors.
The fear may lead people to take protective yet obsessive measures like constantly checking their ears for signs of unwanted visitors.
6. Technophobia: The Threats of Progress

Technophobia, or the fear of technology, can include the use of modern electronic devices such as headphones and audio gear.
This fear is surprisingly common. An estimated one-third of the population experiences some degree of nervousness when faced with new technology.
Several factors can contribute to technophobia. These include social and cultural influences, “doomsday scenarios” shown in media, and bad personal experiences with technology.
The Y2K scare is a prime example of how mass hysteria can fuel the fear of technology.
7. Other Phobias With Audio Triggers

Some phobias, while not directly related to sound, can be triggered by noises associated with the feared object or situation.
For example:
- Musophobia (fear of mice or rats) may be triggered by the squeaking sounds these rodents make.
- Coulrophobia (fear of clowns) can be intensified by the squeaky shoes, laughter, or circus music associated with clowns.
- Agoraphobia (fear of open or crowded spaces) may include a fear of the sounds in these environments, like the murmur of a crowd or traffic noise.
Additionally, the use of headphones, especially noise-canceling ones, can intensify feelings of isolation for those with autophobia or monophobia (fear of being alone).
