You’ve seen the term “active noise cancellation” used to promote wireless headphones, but what is it exactly?
When you have no choice but to be exposed to constant ambient noise, active noise canceling (ANC) headphones can save the day (and your hearing!).
However, if you’re the type who likes to research before jumping into a trend, it’s easy to get lost in all the technical jargon when reading about ANC.
While ANC is technical, understanding its concepts is easy with the right resources. To help you with this, we’ve gathered all the information you need about active noise cancellation. Let’s dive right in.
What Is Active Noise Cancellation?
Active noise cancellation (ANC), reduces unwanted background sounds via phase cancellation. ANC headphones do this by using specialized microphone configurations and signal-processing components.
Standard headphones, on the other hand, rely on passive noise isolation from the ear cups or ear tips to block outside noises from your ears. Cover your ears with the palms of your hands or plug them with your fingers, and voila, you’re experiencing passive noise isolation.
ANC headphones combine passive sound isolation and active noise cancellation, averaging 30 dB of additional noise reduction than non-ANC headphones.
How Does Active Noise Cancellation Work for Headphones?
Headphones enact phase cancellation for their ANC features using two primary components:
- Beamforming microphones are responsible for recording environmental noise.
- A soundcard, frequently a DSP (Digital Signal Processor), receives the noise signal and makes interventions in its phase character.
Here’s the chronological process by which headphones perform ANC:
- Beamforming microphones on the headphones record the listening environment.
- The audio picked up by the microphones gets sent to a DSP in the headphones.
- The DSP flips the phase of the audio that it receives.
- The phase-flipped signal plays through the speakers on the headphones. Phase cancellation occurs as the sound waves from the environment sum with their phase-flipped duplicates produced by the DSP and speakers.
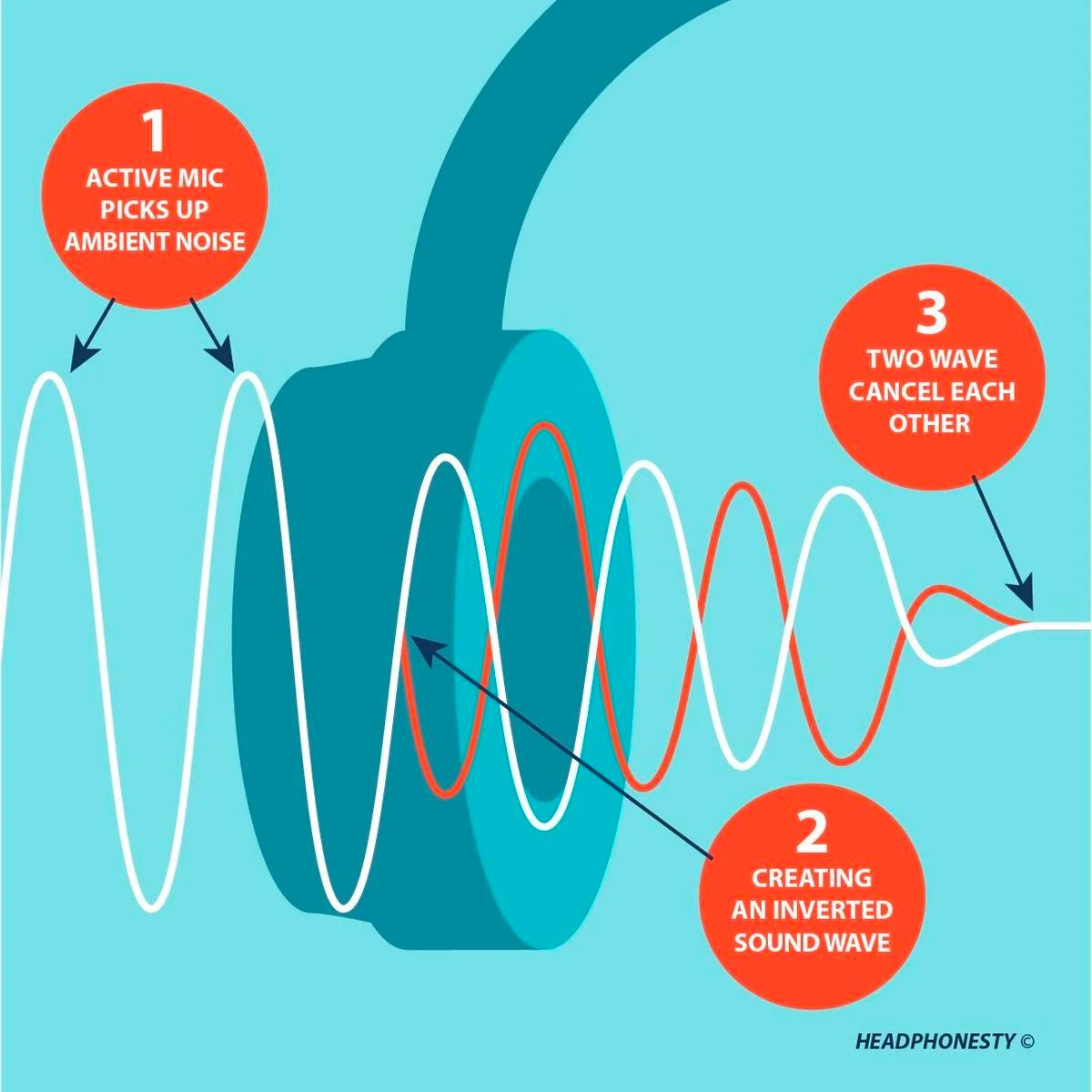
What Is Phase Cancellation?
Phase cancellation is the phenomenon in which identical waves, in opposite phase positions, negate each other’s movements. It is the concept that makes ANC possible.
The diagram below shows two identical waves, with one key difference. The bottom wave’s phase is 180 degrees off from the top wave. Another way to say this is that the bottom wave’s phase has been flipped, or inverted.
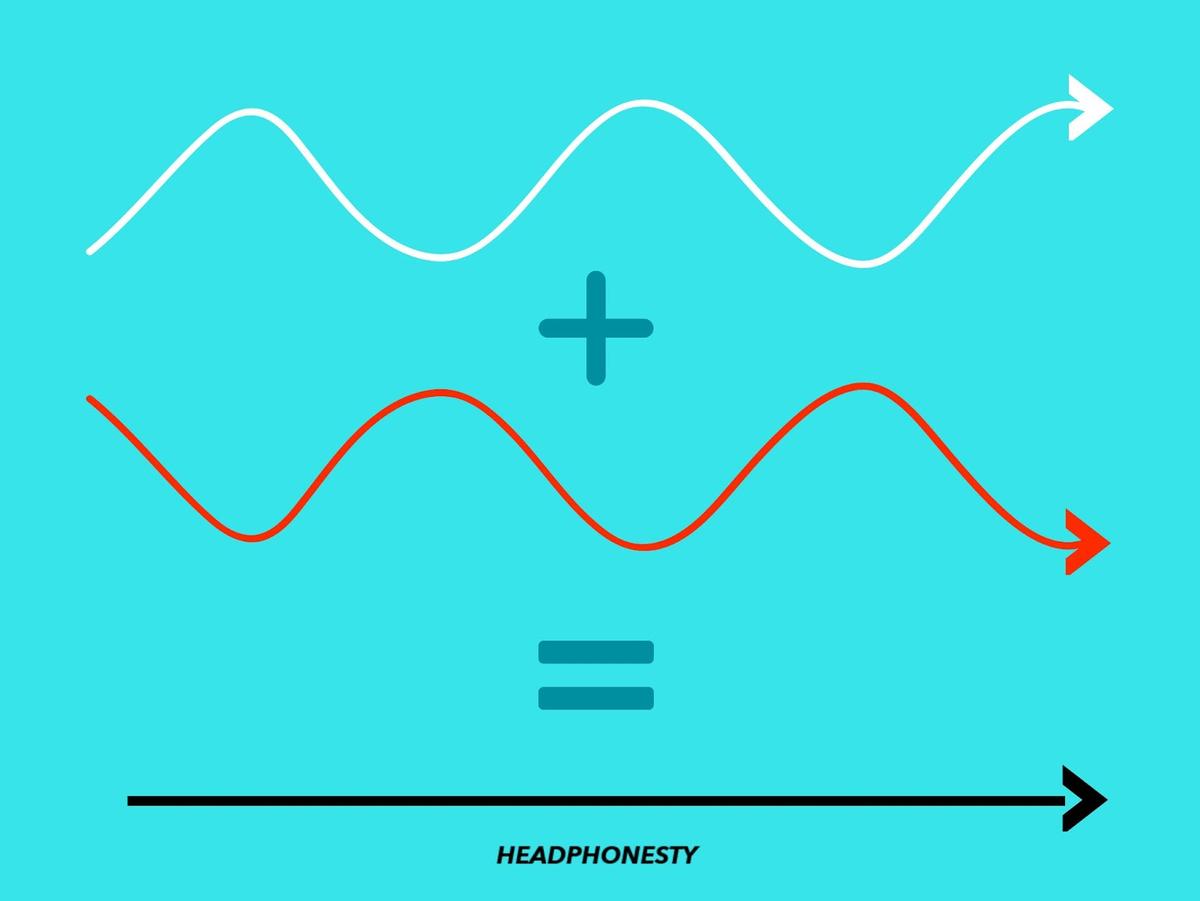
When the top wave compresses, the bottom wave rarifies with equal force, and vice versa. When these waves play simultaneously, their equal and opposite movements cancel each other out.
You can think of phase cancellation as two boxers hitting either side of a punching bag simultaneously with equal force. Since the forces are equal, the punching bag will not move. You can also think of phase cancellation as adding -2 and +2, which results in zero.
Types of ANC Systems
Generally, there are four types of ANC systems:
- Feedback: This setup has a mic inside the ear cup and in front of the speaker. It allows the headphones to hear what you hear and adapt the noise cancellation accordingly. However, it doesn’t work as well for canceling sounds in the 1-2 kHz range.
- Feedforward: The installed mic is on the outer side of the ear cup. It can pick up external noises quickly and produce a phase-flipped signal to counter them.
- Hybrid: This setup combines feedback and feedforward ANC. It uses two mics: one on the outer side of the ear cup and the other in front of the speaker.
- Adaptive: The hardware setup for adaptive ANC is similar to hybrid ANC. But it adds a software processor to automatically adjust the level of noise cancellation based on your surroundings and the headphones’ fit. It was first developed by Qualcomm for true wireless earbuds.
How Well Does ANC in Headphones Cancel Sounds?
Despite how far noise-canceling technology has come, it still can’t block all sounds – especially when there’s no music playing. However, it is much better than solely relying on passive noise isolation.
For context, non-ANC headphones can reduce sounds at mid-to-high frequencies by 15-30 dB depending on the form factor, fit, and ear cup material. However, they’re ineffective at reducing low-frequency sounds (20-800 Hz) like the hum of car engines, air conditioners, or airplane engines.
ANC headphones, on the other hand, can typically block an additional 30 dB of low-frequency noises under 1 kHz. This means that ANC headphones can reduce ambient sounds by up to 60 dB, depending on the implementation of active and passive components.
That’s not to say ANC is flawless. Since ANC works by recording outside noises and processing them prior to their speaker output, latency comes into play.
The shortfalls of ANC
As ANC relies on signal processing to perform its functions, the DSPs in ANC headphones need time to react to the environmental sounds they’re trying to cancel.
Because of this, ANC works best for reducing repetitive noises, like the constant hum of an air conditioner, rather than sudden loud noises, like an ambulance passing by or a dog barking.
ANC’s delayed reaction to processing outside noise is also why it’s more effective at canceling lower frequencies than higher ones. The longer and slower wavelengths of deeper tones grant a DSP more processing time than the short and rapid wavelengths of high-pitched sounds.
Additionally, ANC frequently has trouble isolating noise from crowded spaces. Human speech is unpredictable and high-pitched, which a DSP finds challenging to process.
Despite their checkered efficiency, ANC headphones work well for the general purpose of reducing unwanted noises – and preventing hearing loss, for that matter. So, if you’re constantly around loud noises, consider investing in a good pair of ANC headphones.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How can you get better noise cancellation?
- What is the difference between ANC off and transparency mode?
- Does ANC or transparency use more battery?
- What’s the difference between ANC and ENC?
How can you get better noise cancellation?
Generally, leather-based ear pads work best when it comes to noise isolation. Try to look for headphones with genuine or artificial leather ear pads for maximum noise reduction.
If ANC earbuds are more your style, you should consider the material of the ear tips that you’ll use. Most earbuds come with silicone tips by default, but you might want to swap them out for foam ear tips for optimal noise reduction.
What is the difference between ANC off and transparency mode?
With ANC off, your headphones will simply operate as a standard pair of headphones. The microphones and DSP are on standby, while the cups and pads provide passive noise isolation from external noises.
In transparency mode, the beamforming microphones and soundcard in your headphones actively amplify the sounds in your environment by playing them through the headphone speakers.
Does ANC or transparency use more battery?
Using ANC and transparency mode drains your headphones’ battery faster than just using them to play music. In fact, your headphones will still need batteries to use ANC, even when they’re plugged into your audio source.
What’s the difference between ANC and ENC?
ANC reduces the amount of background noise you hear, while environmental noise cancellation (ENC) reduces the amount that enters your vocal mic. So, ANC is for you, while ENC is for the one you’re talking to on calls.

What type headset do I need for protection from loud lawnmower noises? I already have significant hearing loss in both ears from aircraft engine noises and shooting/gunshot noises.
Thank you.